function函数对象类型的应用
大约 3 分钟
function函数对象类型的应用
function:函数对象类;
- 绑定器、函数对象、lambda表达式实际上都是函数对象。
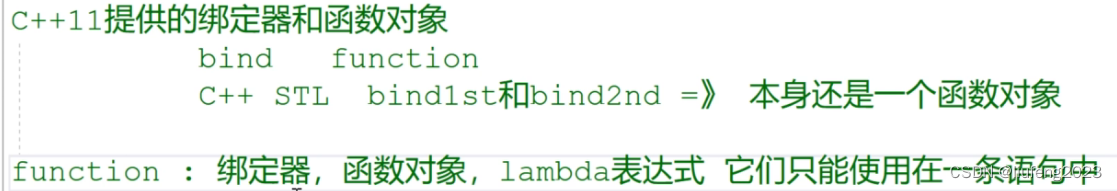
如果我们最终得到的绑定器、函数对象、lambda表达式,这些函数对象,想在多条语句中应用 ,怎么办?如何将这些函数对象的类型留下来?
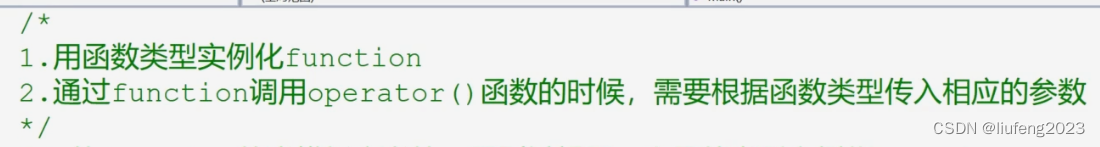
源码中希望你用一个函数类型来实例化function模板。
区别函数类型和函数指针类型:
函数指针类型:
- 是一个,指向返回值是void,不带形参的函数。
void(*)()
函数类型:
- 我们需要用函数类型来实例化function。
- 只给出返回值和参数列表即可
void()
示例
无参函数类型
用函数对象类型func1将hello1函数类型保留下来了,然后就可以使用func1()调用了
void hello1() {
cout << "hello world" << endl;
}
//从function的类模板定义处,看到希望用一个函数类型实例化function
function<void()> func1 = hello1;
func1(); //func1.operator()()=>hello1()
#结果
hello world
有参函数类型
void hello2(string str) //void (*pfunc)(string)
{
cout << str << endl;
}
function<void(string)> func2 = hello2;
func2("hello world2!");//func2.operator()(string str)=>hello2(str)
#结果
hello world2!
int sum(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
function<int(int, int)> func3 = sum;
cout << func3(20, 30) << endl; //50
function不仅仅可以留下,也可以留下。()
function是对一个函数/函数对象的包装
也可以说function是对一个函数/函数对象的包装。
[](int a, int b)->int {return a + b;}是函数对象
function<int(int, int)> func4 = [](int a, int b)->int {return a + b;}
cout << func4(100, 200) << endl; //300
上面是对function作用于全局函数,将其函数类型留下来。
当然,function也可以将类的成员方法留下来!
function也可以将类的成员方法留下来
class Test {
public: //必须依赖一个对象void (Test::*pfunc)(string)
void hello(string str) {
cout << str << endl;
}
};
//成员方法的调用必须依赖一个对象
function<void(Test*, string)> func5 = &Test::hello;
func5(&Test(), "call Test::hello!");
Test*传给了this指针
function使用举例
funtion的作用:
- 保留 的类型,然后再各处都可以使用。

我们使用function,将函数的类型保存下来使用
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <functional>//使用function函数对象类型
#include <algorithm>
#include <ctime>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void doShowAllBooks() { cout << "查看所有书籍信息" << endl; }
void doBorrow() { cout << "借书" << endl; }
void doBack() { cout << "还书" << endl; }
void doQueryBooks() { cout << "查询书籍" << endl; }
void doLoginOut() { cout << "注销" << endl; }
int main()
{
int choice = 0;
map<int, function<void()>> actionMap;
actionMap.insert({ 1, doShowAllBooks });//老版本:insert(make_pair(xx,xx));
actionMap.insert({ 2, doBorrow });
actionMap.insert({ 3, doBack });
actionMap.insert({ 4, doQueryBooks });
actionMap.insert({ 5, doLoginOut });
for (;;)
{
cout << "-----------------" << endl;
cout << "1.查看所有书籍信息" << endl;
cout << "2.借书" << endl;
cout << "3.还书" << endl;
cout << "4.查询书籍" << endl;
cout << "5.注销" << endl;
cout << "-----------------" << endl;
cout << "请选择:";
cin >> choice;
auto it = actionMap.find(choice);//map pair first second
if (it == actionMap.end())
{
cout << "输入数字无效,重新选择!" << endl;
}
else
{
it->second();
}
//不好,因为这块代码无法闭合 无法做到“开-闭原则”
/*switch (choice)
{
case 1:
break;
case 2:
break;
case 3:
break;
case 4:
break;
case 5:
break;
default:
break;
}*/
}
return 0;
}