带引用计数的智能指针
大约 6 分钟
带引用计数的智能指针
shared_ptr和weak_ptr;
带引用计数的好处:。
带引用计数的智能指针是怎么解决多个指针持有一个资源的?
- 带引用计数:
- 当1个智能指针引用这个资源的时候,这个资源相应的引用计数就加1,当这个智能指针出作用域,不再使用这个资源的时候,这个资源的引用计数就减1。
- 当引用计数减1不为0的时候,这个智能指针不使用这个资源了,但是还有其他智能指针在使用这个资源,这个智能指针不能析构这个资源,只能直接走人。
- 当引用计数减1为0的时候,说明当前智能指针是最后使用这个资源的智能指针,所以它要负责这个资源的释放。(完美的解决了智能指针的浅拷贝—就是多个智能指针多次释放同一个资源)
带引用计数的智能指针的实现
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
//对资源进行引用计数的类
template<typename T>
class RefCnt
{
public:
RefCnt(T* ptr = nullptr)
:mptr(ptr)
{
if (mptr != nullptr)
{
mcount = 1;
}
}
void addRef() { mcount++; } //增加资源的引用计数
int defRef() { return --mcount; }
void show() { cout << mcount << endl; }
private:
T* mptr;
//int mcount;
atomic_int mcount;
};
template<typename T>
class CSmartPtr
{
public:
CSmartPtr(T* p = nullptr)
:ptr(p)
{
mpRefCnt = new RefCnt<T>(ptr);
}
~CSmartPtr()
{
if (0 == mpRefCnt->defRef())
{
delete ptr;
ptr = nullptr;
}
}
T& operator*()
{
return *ptr;
}
T* operator->()
{
return ptr;
}
void Count() { return mpRefCnt->show(); }
CSmartPtr(const CSmartPtr<T>& src)
:ptr(src.ptr), mpRefCnt(src.mpRefCnt)
{
if (ptr != nullptr)
{
mpRefCnt->addRef();
}
}
CSmartPtr<T>& operator=(const CSmartPtr<T>& src)
{
if (this == &src)
{
return *this;
}
//检查自己原先指向的资源,因为自己要改变指向了,如果执行delRef后,引用计数为0的话,就释放资源;
if (0 == mpRefCnt->defRef())
{
delete ptr;
}
ptr = src.ptr;
mpRefCnt = src.mpRefCnt;
mpRefCnt->addRef();
return *this;
}
private:
T* ptr; //指向资源的指针
RefCnt<T>* mpRefCnt; //指向该资源引用计数的类
};
int main()
{
CSmartPtr<int>p(new int(50));
CSmartPtr<int>q(p);
cout << *p << endl;
cout << *q << endl;
p.Count();
cout << p.operator->() << endl;
return 0;
}
上面的CSmartPtr和标准的shared_ptr的区别是:
- ;
- shared_ptr将m_count定义成
库中的shared_ptr和weak_ptr都是线程安全的,可以直接使用在多线程的环境下。
shared_ptr的交叉引用问题

观察,强智能指针观察

强智能指针循环引用(交叉引用)是什么问题?什么结果?怎么解决?
class B;
class A
{
public:
A() { cout << "A()构造" << endl; }
~A() { cout << "~A()析构" << endl; }
shared_ptr<B> ptr2;
};
class B
{
public:
B() { cout << "B()构造" << endl; }
~B() { cout << "~B()析构" << endl; }
shared_ptr<A> ptr1;
};
int main()
{
shared_ptr<A> pa(new A());
shared_ptr<B> pb(new B());
cout << pa.use_count() << endl;//1
cout << pb.use_count() << endl;//1
pa->ptr2 = pb;
pb->ptr1 = pa;
cout << pa.use_count() << endl;//2
cout << pb.use_count() << endl;//2
}
- 出main函数作用域,pb先析构(将B资源的引用计数从2减为1),再析构pa(将A资源的引用计数从2减为1),此后,AB对象的引用计数均为1,对象不能析构;
- 产生的问题:new出来的资源无法释放,造成问题。

解决办法:
class B;
class A
{
public:
A() { cout << "A()构造" << endl; }
~A() { cout << "~A()析构" << endl; }
weak_ptr<B> ptr2; //引用对象的地方使用 弱智能指针
};
class B
{
public:
B() { cout << "B()构造" << endl; }
~B() { cout << "~B()析构" << endl; }
weak_ptr<A> ptr1; //引用对象的地方使用 弱智能指针
};
int main()
{
shared_ptr<A> pa(new A()); //定义对象 使用强智能指针
shared_ptr<B> pb(new B());
pa->ptr2 = pb;
pb->ptr1 = pa;
cout << pa.use_count() << endl;//1
cout << pb.use_count() << endl;//1
}
。

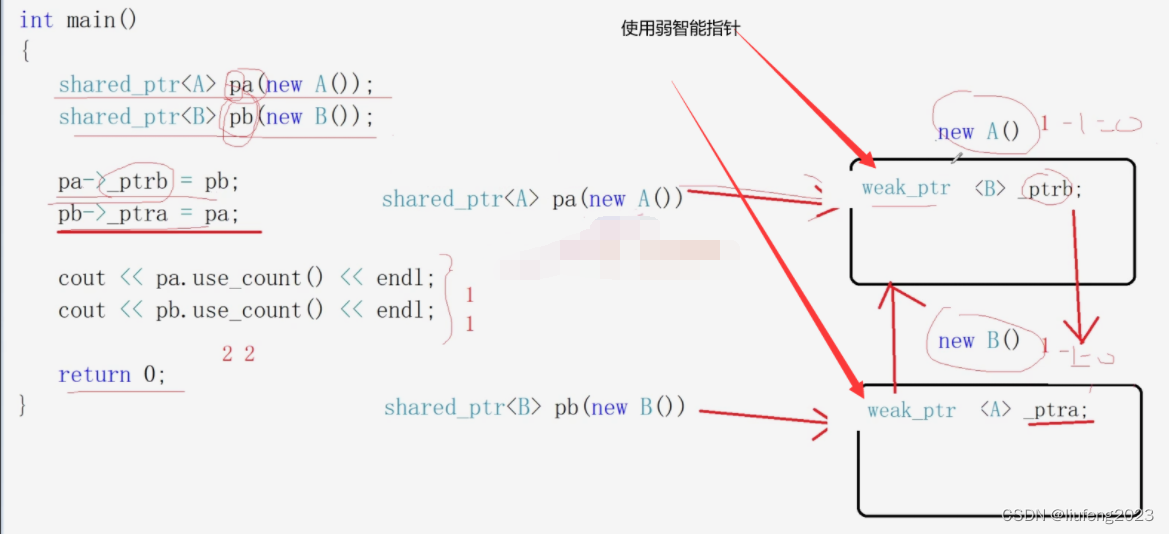
可以正常释放资源!
weak_ptr怎么使用资源
class B;
class A
{
public:
A() { cout << "A()构造" << endl; }
~A() { cout << "~A()析构" << endl; }
weak_ptr<B> ptr2;
void testA() { cout << "非常好的方法" << endl; }
};
class B
{
public:
B() { cout << "B()构造" << endl; }
~B() { cout << "~B()析构" << endl; }
void func() {
//_ptr1->testA(); //弱智能指针是无法调用A类的testA函数的;
}
weak_ptr<A> ptr1; //引用对象的地方使用 弱智能指针
};
- 弱智能指针只会观察资源,不能使用资源;
- ,不能将弱智能指针当成裸指针看待。
怎么解决弱指针指针不能调用函数的问题?
- 。
class B;
class A
{
public:
A() { cout << "A()构造" << endl; }
~A() { cout << "~A()析构" << endl; }
weak_ptr<B>ptr2;
void testA() { cout << "非常好的方法" << endl; }
};
class B
{
public:
B() { cout << "B()构造" << endl; }
~B() { cout << "~B()析构" << endl; }
void func()
{
shared_ptr<A>ps = ptr1.lock();
if (ps != nullptr) //有可能提升成功,也有可能失败,需要判断
{
ps->testA();
}
cout << ps.use_count() << endl;//智能指针ps提升成功,引用技术加1到2
//智能指针ps出函数作用域自动析构,引用计数从2减到1
}
weak_ptr<A>ptr1;
};
int main()
{
shared_ptr<A>ptra(new A());
shared_ptr<B>ptrb(new B());
ptra->ptr2 = ptrb;
ptrb->ptr1 = ptra;
cout << ptra.use_count() << endl;//1
cout << ptra.use_count() << endl;//1
ptrb->func();
cout << ptra.use_count() << endl;//1
cout << ptra.use_count() << endl;//1
ptrb->func();
}
- 在多线程中,弱智能指针观察的资源有可能被释放,有可能没有被释放,;
- 弱智能指针需要使用对象,需要从一个观察者提升为强智能指针,在提升的过程中有可能提升失败,资源已经释放了;有可能提升成功,资源还没释放。