派生类对象间的复制控制
大约 4 分钟
派生类对象间的复制控制
从前面的知识,我们知道,基类的拷贝构造函数和operator=运算符函数不能被派生类继承,那么在执行派生类对象间的复制操作时,就需要注意以下几种情况:
- 如果用户定义了基类的拷贝构造函数,而的拷贝构造函数,那么在用一个派生类对象初始化新的派生类对象时,两对象间的**执行缺省的行为**(只拷贝值),而两对象间的**执行用户定义的基类拷贝构造函数**。
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
class Base
{
public:
Base()
: _pbase(nullptr)
{
cout << "Base()" << endl;
}
Base(const char *pbase)
: _pbase(new char[strlen(pbase) + 1]())
{
cout << "Base(const char *)" << endl;
strcpy(_pbase, pbase);
}
Base(const Base &rhs)
: _pbase(new char[strlen(rhs._pbase) + 1]())
{
cout << "Base(const Base &)" << endl;
strcpy(_pbase, rhs._pbase);
}
Base &operator=(const Base &rhs)
{
cout << "Base &operator=(const Base &)" << endl;
if(this != &rhs)
{
delete [] _pbase;
_pbase = nullptr;
_pbase = new char[strlen(rhs._pbase) + 1]();
strcpy(_pbase, rhs._pbase);
}
return *this;
}
~Base()
{
cout << "~Base()" << endl;
if(_pbase)
{
delete [] _pbase;
_pbase = nullptr;;
}
}
friend std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Base &rhs);
private:
char *_pbase;
};
std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Base &rhs)
{
if(rhs._pbase)
{
os << rhs._pbase;
}
return os;
}
class Derived
: public Base
{
public:
Derived(const char *pbase)
: Base(pbase)
{
cout << "Derived(const char *)" << endl;
}
~Derived()
{
cout << "~Derived()" << endl;
}
friend std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Derived &rhs);
};
std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Derived &rhs)
{
const Base &ref = rhs;
os << ref;
return os;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
Derived d1("hello");
cout << "d1 = " << d1 << endl;
cout <<endl << endl;
Derived d2 = d1;
cout << "d1 = " << d1 << endl;
cout << "d2 = " << d2 << endl;
cout <<endl << endl;
Derived d3("world");
cout << "d3 = " << d3 << endl;
cout << endl << endl;
d3 = d1;
cout << "d1 = " << d1 << endl;
cout << "d3 = " << d3 << endl;
return 0;
}
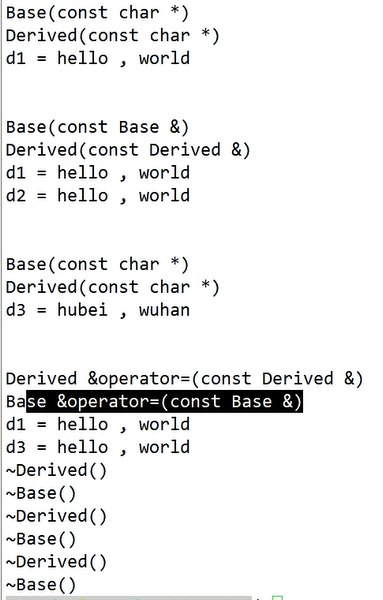
调用的是基类的拷贝构造和拷贝赋值

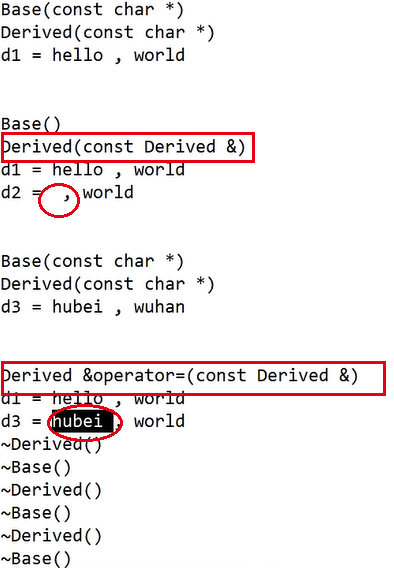
- 如果用户定义了派生类的拷贝构造函数或者重载了派生类的对象赋值运算符=,则在用已有派生类对象初始化新的派生类对象时,或者在派生类对象间赋值时,将会执行用户定义的派生类的拷贝构造函数或者重载赋值函数,而不会再自动调用基类的拷贝构造函数和基类的重载对象赋值运算符,这时,通常用户在派生类的拷贝构造函数或者派生类的赋值函数中基类的拷贝构造或赋值运算符函数。
//派生类的拷贝构造函数或者派生类的赋值函数中 没有显式调用 基类的拷贝构造或赋值运算符函数
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
class Base
{
public:
Base()
: _pbase(nullptr)
{
cout << "Base()" << endl;
}
Base(const char *pbase)
: _pbase(new char[strlen(pbase) + 1]())
{
cout << "Base(const char *)" << endl;
strcpy(_pbase, pbase);
}
Base(const Base &rhs)
: _pbase(new char[strlen(rhs._pbase) + 1]())
{
cout << "Base(const Base &)" << endl;
strcpy(_pbase, rhs._pbase);
}
Base &operator=(const Base &rhs)
{
cout << "Base &operator=(const Base &)" << endl;
if(this != &rhs)
{
delete [] _pbase;
_pbase = nullptr;
_pbase = new char[strlen(rhs._pbase) + 1]();
strcpy(_pbase, rhs._pbase);
}
return *this;
}
~Base()
{
cout << "~Base()" << endl;
if(_pbase)
{
delete [] _pbase;
_pbase = nullptr;;
}
}
friend std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Base &rhs);
private:
char *_pbase;
};
std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Base &rhs)
{
if(rhs._pbase)
{
os << rhs._pbase;
}
return os;
}
class Derived
: public Base
{
public:
Derived(const char *pbase, const char *pderived)
: Base(pbase)
, _pderived(new char[strlen(pderived) + 1]())
{
cout << "Derived(const char *)" << endl;
strcpy(_pderived, pderived);
}
Derived(const Derived &rhs) //拷贝构造
: _pderived(new char[strlen(rhs._pderived) + 1]())
{
cout << "Derived(const Derived &)" << endl;
strcpy(_pderived, rhs._pderived);
}
Derived &operator=(const Derived &rhs) //拷贝赋值
{
cout << "Derived &operator=(const Derived &)" << endl;
if(this != &rhs)
{
delete [] _pderived;
_pderived = nullptr;
_pderived = new char[strlen(rhs._pderived) + 1]();
strcpy(_pderived, rhs._pderived);
}
return *this;
}
~Derived()
{
cout << "~Derived()" << endl;
if(_pderived)
{
delete [] _pderived;
_pderived = nullptr;;
}
}
friend std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Derived &rhs);
private:
char *_pderived; //派生类的数据部分
};
std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Derived &rhs)
{
const Base &ref = rhs;
os << ref << " , " << rhs._pderived;
return os;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
Derived d1("hello", "world");
cout << "d1 = " << d1 << endl;
cout <<endl << endl;
Derived d2 = d1;
cout << "d1 = " << d1 << endl;
cout << "d2 = " << d2 << endl;
cout <<endl << endl;
Derived d3("hubei", "wuhan");
cout << "d3 = " << d3 << endl;
cout << endl << endl;
d3 = d1;
cout << "d1 = " << d1 << endl;
cout << "d3 = " << d3 << endl;
return 0;
}
派生类定义了后,就不会再调用基类的
//派生类的拷贝构造函数或者派生类的赋值函数中 显式调用 基类的拷贝构造或赋值运算符函数
class Derived
: public Base
{
public:
//...
Derived(const Derived &rhs)
: Bas e(rhs)//显示调用基类的拷贝构造函数
, _pderived(new char[strlen(rhs._pderived) + 1]())
{
cout << "Derived(const Derived &)" << endl;
strcpy(_pderived, rhs._pderived);
}
Derived &operator=(const Derived &rhs)
{
cout << "Derived &operator=(const Derived &)" << endl;
if(this != &rhs)
{
Base::operator=(rhs);//显示的调用基类的赋值运算符函数
delete [] _pderived;
_pderived = nullptr;
_pderived = new char[strlen(rhs._pderived) + 1]();
strcpy(_pderived, rhs._pderived);
}
return *this;
}
};